The Indian government has outlined a comprehensive strategy to enhance agricultural productivity and resilience through initiatives such as research infrastructure review, development of climate-resilient crop varieties, promotion of natural farming among one crore farmers, and establishment of bio-input resource centres.
Additionally, efforts include achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds, developing vegetable production clusters, implementing Digital Public Infrastructure in agriculture, and supporting shrimp farming through NABARD. These initiatives aim to modernize agriculture and ensure sustainable growth across the sector. let’s summarize each strategy briefly and discuss how government schemes have progressed in these areas.

1. NATURAL FARMING
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman prioritized agriculture in the Union Budget, proposing to train 1 crore farmers in natural farming to enhance productivity, sustainability, and access to premium markets for organic produce. This initiative aims to provide farmers with certifications and branding, facilitating a shift towards sustainable agriculture.
WHAT IS NATURAL FARMING
Natural Farming can be defined as “chemical- free and livestock-based farming”. Soundly grounded in agro-ecology, it is a diversified farming system that integrates crops, trees and livestock, allowing the optimum use of functional biodiversity. Natural Farming holds the promise of enhancing farmers’ income while delivering many other benefits, such as restoration of soil fertility and environmental health, and mitigating and/or reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Natural Farming in India
Bharatiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhati (BPKP) is a sub-mission under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY), which falls within the umbrella of the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
BPKP aims at promoting traditional indigenous practices, which give freedom to farmers from externally purchased inputs. It focuses on on-farm biomass recycling with major stress on biomass mulching; use of cow dung–urine formulations; and exclusion of all synthetic chemical inputs either directly or indirectly.
The scheme has a total outlay of Rs 4645.69 crore for the period of six years (2019-20 to 2024-25).
2. Government Initiatives for Self-Sufficiency in Pulses and Oilseeds
Achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds has been a priority for the Indian government, supported by various initiatives and schemes:
National Food Security Mission- Oilseeds (NFSM-OS)
National Food Security Mission- Oilseeds (NFSM-OS) is being implemented by the Government of India to augment the availability of edible oils and reduce the import burden by increasing the production and productivity of in the country.
Economic Survey says that in 2022-23, oilseeds production reached 41.4 million tonnes. The domestic availability of edible oil has risen from 86.30 lakh tonnes in 2015-16 to 121.33 lakh tonnes in 2023-24. This has reduced the percentage share of imported edible oil, from 63.2 per cent to 57.3 percent .
Minimum Support Price (MSP) For Pulses and Oilseeds
The increased Minimum Support Prices (MSP) for the 2024-25 Kharif season by the Union Cabinet signifies a robust commitment to bolstering the agricultural sector and ensuring the economic well-being of farmers. This year’s significant hikes, especially for oilseeds and pulses, underscore the government’s focus on enhancing profitability and sustainability in farming.
Trends of MSP for Pulses
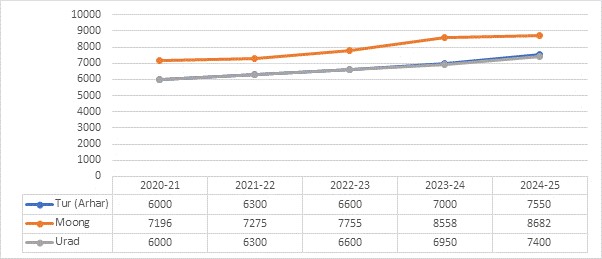
Trends of MSP for Oilseed

3. High-Yielding and Climate-Resilient Varieties: The Need of the Hour in IndiaTop of Form
Bottom of Form
The Indian government has announced a significant initiative to introduce 109 new high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties across 32 field and horticulture crops, aimed at revolutionizing agricultural practices nationwide. These new varieties are meticulously developed to withstand diverse climatic conditions while enhancing crop productivity and ensuring sustainability.
During 2014-15 to 2023-24, a total of 2593 high-yielding varieties were released which include 2177 climate resilient (83% of total) with biotic and abiotic stress resistance, and 150 bio-fortified crop varieties. More than 1.0 lakh quintal breeder seed on more than 2200 varieties of 56 crops is being produced. Deployment of climate resilient technologies led to enhanced production even during the abnormal years
4. Transforming Agriculture: DPI Initiative to Revolutionize Digital Crop SurveysTop of FormBottom of Form
The government’s initiative to implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture aims to revolutionize the sector by leveraging digital technology to benefit farmers and enhance agricultural efficiency. Buoyed by the success of pilot projects, this nationwide initiative will be carried out in collaboration with state governments over a span of three years.
As part of the initial phase, a digital crop survey will be conducted during the Kharif season in 400 districts. This survey will utilize the DPI to collect detailed data on crop cultivation patterns, land use, and yield estimates. By digitizing these aspects, the government can enhance precision in planning and implementing agricultural strategies, including distribution of subsidies, insurance coverage, and disaster management.
5. Jan Samarth Initiative: Empowering Farmers with Accessible Kisan Credit Cards
Jan Samarth based Kisan Credit Cards” refers to a scheme designed to provide Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) to farmers with simplified and accessible criteria. The objective is to ensure that farmers, especially those in need of financial assistance, can easily obtain credit through these cards.
The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) has streamlined agricultural credit accessibility. As of January 31, 2024, banks issued 7.5 crores KCC with a limit of ₹9.4 lakh crores. As a further measure, the KCC was extended to meet the working capital needs of fisheries and animal husbandry activities in 2018-19, along with the enhancement of the limit for collateral-free loans to ₹1.6 lakh. In the case of a Tri-Partite Agreement (TPA) among borrowers, milk unions, & banks, the collateral-free loan can go up to ₹3 lakh.25 As of March 31, 2024, 3.49 lakh KCC and 34.5 lakh KCC were issued to fisheries and animal husbandry activities, respectively.
6. Strengthening India’s Shrimp Industry: Enhanced Breeding and Financial Support
India is currently, the 2nd largest fish producing country with around 8% share in global fish production and a record high fish production of 174.45 lakh tonnes (2023-24). India also stands at 2nd in aquaculture production and is one of the top shrimp producing and seafood exporting nations in the world. The sector provides sustainable livelihoods to over 30 million people mostly within the marginalized and vulnerable communities.
To ensure availability of quality brood for quality seed, Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman announced the financial support for setting up a network of Nucleus Breeding Centre (NBC) for shrimp brood stocks. Further, financing for shrimp farming, processing and export will be facilitated through NABARD.
Establishment of state-of-art facilities in NBCs will improve the genetic quality of aquaculture species for higher productivity and quality, reduce the dependence on import of shrimp brood stock. This is a welcoming step to promote the shrimp industry, as shrimp is a major contributor to seafood export. Shrimp exports have significantly growth to Rs. 40,013 crore in 2023-24 from Rs. 8,175 Crore in 2011. In 2023-24, the export of frozen shrimp was to the tune of 7.16 lakh ton worth Rs. 40,013 crore.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
Conclusion
The government’s holistic agricultural strategy aims to boost productivity and resilience through research and development, introducing new high-yielding crop varieties. It prioritizes natural farming initiatives for one crore farmers, builds bio-input centers, and works towards achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds. Initiatives such as Digital Public Infrastructure and support for shrimp breeding centers underscore efforts to modernize and enhance agricultural practices nationwide.Top of Form

Comments are closed.